Coast of the Caspian. Caspian Sea
The pearl of unique beauty and originality is the Caspian Sea. This is a unique, the only enclosed body of water in the world with a fragile and priceless ecosystem. Its uniqueness attracts worldwide attention. The Caspian is considered the largest inland water body in the world, located at the junction of Asia and Europe. Poets, philosophers, historians, geographers devoted a lot of their works to the amazing natural creation. Among them: Homer, Herodotus, Aristotle. The biological environment of the Caspian Sea is also unique. But first things first. We invite you to find out about the depth, level, location of this reservoir, which countries are washed by the Caspian Sea. Well, let's go...

Historical references
Many are interested in where the Caspian Sea is located, the history of its occurrence. But few people know that it is of oceanic origin. Thirteen million years ago, this place was the bottom of the ocean. As a result of natural disasters, the Alps arose and separated the Sarmatian Sea from the Mediterranean. 5 million years passed, and the Sarmatian Sea was divided into smaller water bodies, which included the Black and Caspian Seas. For a long time there were connections and separations of waters. And 2 million years ago the Caspian Sea was completely cut off from the World Ocean. This was the beginning of its formation. History confirms that during the period of formation, the depth and area of the Caspian Sea changed several times.
Today, the Caspian is classified as the largest endorheic lake. Because of its huge size, it is commonly called the sea. And also due to the fact that it was formed on the earth's crust of the oceanic type.
Today the Caspian makes up 44% of the planet's lake waters. During its formation, different tribes and peoples gave the lake about 70 names. The Greeks called it the Hyrcanian (Dzhurdzhansky) lake from the name of the city of Gorgan and the province of Hyrkania. The ancient Russians called it the Khvalyn Sea, from the name of the Khvalis people who lived in the coastal area. Arabs, Persians, Azerbaijanis, Turks, Crimean Tatars called it the Khazar Sea. Once upon a time, in the delta of the Kura River, which flows into the reservoir, there was an island and a city, after which it was called the Abeskun Sea. Later this city was flooded. There was also the name Saray Lake. In honor of the city of Derbant (Dagestan), it was called the Derbent Sea. There was also the name Sihai and others.

Geographic location
Many people want to know where the Caspian Sea is located on the map. This place is located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. The physical and geographical conditions of the sea allow us to divide it into three parts:
- The share of the Northern Caspian occupies 25% of the reservoir.
- The Middle Caspian zone has 36%.
- The component of the southern part of the lake is 39%.
The Northern and Middle Caspian separates the island of Chechnya from Cape Tyub-Karagan. The Middle and South Caspian divides Chilov Island with Cape Gan-Gulu.
The territory adjacent to the lake is called the Caspian Sea. The size of the Caspian Sea is amazing. The coastline stretches for approximately 6,500 to 6,700 kilometers. The shores have a low-lying and smooth structure. northern part coastline cut water channels and islands of the Ural and Volga deltas. The shores are mostly low and swampy, covered with thickets. The east coast has a limestone structure. In the west, the coast is very winding.
Relief and depth, area of the Caspian Sea
These figures fluctuate constantly. As a result, they affect the sea level. The Caspian Sea thus changes the area and volume of water. If its level is 26.75 km, then the area is 371,000 km 2. And what is the maximum and average depth of the Caspian Sea? In terms of maximum depth, it is second only to Baikal and Tanganyika. The maximum depth in the South Caspian depression is 1,025 m. The bathygraphic curve helps to calculate the average depth of the Caspian Sea, which indicates a depth of 208 m. In the north, the reservoir is shallower - 25 m. The Middle Caspian has many deep depressions, continental slopes, and shelves. Here, the average depth reaches 192 m. The Derbent depression has a depth of 788 m.
The length of the lake from north to south is 1,200 km, and the width of the Caspian Sea from west to east is up to 435 km. The relief of the northern part of the lake is flat, with accumulative islands and banks. The southern part of the Caspian shelf is rich in shell sands, deep water areas with silty sediments. Sometimes bedrocks come out here.
Peninsulas, islands and bays of the Caspian Sea
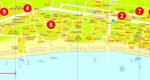
A number of large peninsulas are located on the area of the Caspian Sea. On the west coast, near Azerbaijan, is the Absheron Peninsula. It is here that the cities of Baku and Sumgayit are located. On the eastern side (the territory of Kazakhstan) is the Mangyshlak Peninsula. The city of Aktau was built here. It is also worth noting the following large peninsulas: Miankale, Tyub-Karagan, Buzachi, Agrakhan Peninsula.
The total area of large and medium-sized Caspian islands is 350 km2. There are about 50 such islands. The largest and most famous are: Ashur-Ada, Garasu, Chechen, Chigil, Gum, Dash-Zira, Ogurchinsky and others.
Such a huge body of water cannot exist without bays. Agrakhan, Kizlyar, Mangyshlak, Kazakh bays are known. It is also worth remembering Kaydak Bay, Kenderli, Turkmen, Astrakhan, Gasan-Kuli, Anzeli.
A special bay-lagoon of the Caspian Sea is considered salt Lake Kara-Bogaz-Gol. In 1980, a dam was built that separates this strait from the Caspian Sea. Every year, 8-10 km 3 of water enters Kara-Bogaz-Gol from the Caspian Sea.

What countries are washed by the Caspian Sea?
The Intergovernmental Economic Conference of the Caspian States has established that five coastal countries are washed by the Caspian Sea. What exactly? In the north, northeast and east it borders on Kazakhstan. The coastline is 2,320 km. Who borders the Caspian Sea in the south? This is Iran with a coastline of 724 km. In the southeast, Turkmenistan is located with a coastline of about 1,200 km. The northwest and west of the Caspian is occupied by Russia with a length of 695 km. Azerbaijan stretches for 955 km in the southwest. Here is such a kind of "Caspian Five".

Coastline and nearby cities
Many cities, ports and resorts are located on the Caspian Sea. In Russia, the largest objects are considered: Kaspiysk, Makhachkala, Izberbash, Lagan, Dagestan Lights, Derbent. Astrakhan is the largest port city of the Caspian Sea, located in the Volga delta (60 km from the northern coast).
Baku is considered the largest port city in Azerbaijan. Its location falls on the southern part of the Absheron Peninsula. The city is home to 2.5 million people. Sumgayit is located a little to the north. Lankaran is located near the southern border of Azerbaijan. In the south-east of the Absheron Peninsula there is a settlement of oil workers - Oil Rocks.
In Turkmenistan, on the northern shore of the Krasnovodsk Bay, there is the city of Turkmenbashi. A large resort of this country is Avaza.
In Kazakhstan, the port city of Aktau was built near the Caspian Sea. To the north, in the delta of the Ural River, Atyrau is located. In Iran, on the southern coast of the reservoir, Bandar Anzeli is located.
Rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea
130 large and small rivers flow into the Caspian. Nine of them have a deltoid mouth. Among the largest rivers, we single out the Volga, Ural, Terek, Samur, Sulak, Emba, Kura, Atrek. The largest river flowing into the reservoir is the Volga. For a year, on average, 215-224 km 3 of water flows out of it. All of the above rivers replenish the annual water supply of the Caspian by 88-90%.

Currents, flora and fauna of the Caspian
For those who are interested in where the Caspian Sea flows into, the answer is already clear - it is a closed body of water. Water circulates in it thanks to winds and drains. Most of the water flows into the Northern Caspian, so the northern currents circulate there. These intense currents carry water to the western coast of the Absheron Peninsula. There, the current passes into two branches - one moves parallel to the western coast, the other - to the east.
The fauna of the Caspian basin is represented by 1810 animal species. 415 of them are representatives of vertebrates. About 100 species of fish swim in the Caspian Sea, a large number of sturgeons. Freshwater fish are also found here, represented by pike perch, carp, and roach. Also in the sea there are a lot of carp, mullet, sprat, kutum, bream, salmon, perch, pike. It is worth remembering another inhabitant - the Caspian seal.
The flora of the Caspian Sea and the coastal zone includes 730 species. It is important to note that the reservoir is overgrown with blue-green, diatoms, red, brown, chara algae. The most common are flowering algae - ruppia and zostera. The age of the Caspian flora refers to the Neogene period. Many plants came to the Caspian with the help of ships or conscious human actions.

Research work
Between 285 and 282 B.C. The Greek king Seleucus I ordered the geographer Patroclus the Macedonian to explore the Caspian Lake. Later this work was continued by order of Peter the Great. For this, an expedition was specially organized, led by A. Bekovich-Cherkassky. Later, the research was continued by the expedition of Carl von Werden. Also, the following scientists were engaged in the study of the Caspian Sea: F.I. Simonov, I.V. Tokmachev, M.I. Voinovich.
At the end of the 19th century, I.F. Kolodkin, later - N.A. Ivashentsev. In the same period, N.M. studied the hydrology and hydrobiology of the Caspian Sea for 50 years. Knipovich. 1897 was marked by the founding of the Astrakhan research station. At the beginning of the Soviet era, the Caspian was studied by I.M. Gubkin and other geologists. They directed their work to the search for oil, the study of the aquatic environment, changes in the level of the Caspian Sea.

Economic sphere, shipping, fishing
Many deposits of gas and oil have been found in the Caspian. Scientists have proven that there are about 10 billion tons of oil resources here, and together with gas condensate - 20 billion tons. Since 1820, oil has been extracted on the Absheron shelf, near Baku. Then oil production on an industrial scale began to be engaged in other areas. Oil production from the bottom of the Caspian Sea began in 1949, at Neftyanye Kamni. The long-awaited oil well was drilled by Mikhail Kaverochkin. In addition to oil and gas, salt, limestone, stone, sand, and clay are mined in the Caspian.
Shipping is also given enough attention. Ferry crossings are constantly operating. The most famous destinations are: Baku - Aktau, Makhachkala - Aktau, Baku - Turkmenbashi. Through the Don, Volga and the Volga-Don Canal, the Caspian Lake is connected with Sea of Azov.
Local residents catch sturgeon, bream, carp, pike perch, sprat in the waters of the sea. They are engaged in seal fishing and caviar production. Unfortunately, in this reservoir you can also encounter illegal sturgeon fishing and caviar extraction. The flounder, mullet, different types of shrimp caught here are popular. Sturgeons feed here on the Nereis worm, which was specially brought to the Caspian Sea. The "Five" countries of the Caspian Sea, washed by its waters, specially organize fish breeding and spawning farms.
Sturgeons are the most numerous in the northern shallow waters, especially near Russia. It is worth listing the sterlet, beluga, sturgeon, thorn, stellate sturgeon living there. Many people like to catch carp species: bream, roach, asp. A lot of catfish, grass carp, silver carp live here. There are more small inhabitants in the Caspian than large ones. In the south of the lake, herring winters and spawns. Fishing in the Caspian is allowed all year round, except April-May. They are allowed to use fishing rods, spinning rods, donks and other devices.
Most of all, the Astrakhan region is chosen for fishing in Russia. Catching some sturgeons is temporarily prohibited here, but you can catch pike, catfish, pike perch. In spring, sabrefish and rudd often peck here. In Kalmykia, industrial fishing is carried out in Lagan. Large specimens of carp are found here. Often fishermen have to spend the night right in the boats. The water in these areas is very clear, so spearfishing is used.

Rest on the Caspian Sea
Sandy beaches, mineral waters, therapeutic mud of the Caspian coast are a good help for treatment and relaxation. The tourism industry and resorts here are not as developed as on the Black Sea, but there are many who want to relax. It is at a fairly popular level in Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Iran and Russian Dagestan. Azerbaijan has developed resort area near Baku. Only locals rest here, mainly, foreign tourists lack a sufficient level of service and good advertising.
The Russian coast is mainly located in Dagestan. Potential tourists are afraid to go here. But the beauty of the Caspian is simply mesmerizing! It is here that you can admire the waves with gray scallops, the bitter salinity of dark water, small shells on the shore. Rest on the Caspian Sea is often considered exotic. It's more like a lake...
The increased salinity of the water in the Caspian increases its medicinal properties. The water in the reservoir warms up early, so you can safely come here in May. In September, you can have a great time, because the water is kept at around +21°C.
What are the conditions for recreation in Dagestan near the sea? Here the coast is covered with yellow velvety sea sand. The water of the Caspian Sea warms up faster than in the Black Sea, because the former is much shallower. The swimming season here begins in mid-May. The beauty of the Caspian coast is complemented by picturesque mountains, not far from Derbent. Here you can admire the oldest marine fossils, which were raised by gas formation to a thousand-meter height. After that, many caves were formed here, about which there are various legends. Many locals come to these places to worship higher powers.
During the Soviet period, Dagestan was a holiday destination for tourists from different parts of the USSR. Holidays here are cheaper than on Black Sea coast, the sea is warmer and the sandy shore is more pleasant.

Caspian coast in Dagestan it has many kilometers of beaches: Makhachkala, Samur, Manas, Kayakent. On their territory there are recreation centers (150 units), boarding houses, sanatoriums, children's camps. You can book rooms not only in state hotels, boarding houses, but also in large and small private hotels. Renting a single room here costs from 500 to 1,000 rubles, a double room - 700-1,500 rubles, a luxury apartment - 1,500-2,000 rubles.
If you get tired of swimming in the sea, then in Dagestan you can go to the peaks covered with snow caps. Rafting enthusiasts can go to fast mountain rivers. Guides offer interesting excursions by historical places.
Not far from the Caspian coast, it is worth seeing the capital of Dagestan - Makhachkala. This beautiful and well-equipped city has a highly developed infrastructure. Residents of Makhachkala are trying to attract as many tourists as possible to their city and are building a resort area. Cote d'Azur". This building occupies 300 hectares of area.
The South Dagestan coast with the center in Derbent is the most attractive place for tourism. This area has a temperate continental climate, being in the subtropics. The territory is rich in citrus fruits, figs, pomegranates, almonds, walnuts, grapes and other crops.
No less colorful city of Izberbash. Here beautiful nature with clean mountain-sea air, saturated with the aroma of forests that grow low on the foothills of the Greater Caucasus. The sandy beach can be changed for a walk to mineral springs, among which there are geothermal, contributing to the restoration of health.
Rostourism has taken measures to develop cruise holidays in the Caspian. Thought out not only domestic routes, but also international ones. Often cruises on the sea are joined with the route along the Volga. For such events, very good vessels are needed, because there are often storms on the Caspian Sea.
Another direction sea recreation in the Caspian Sea is health and medical. Many ailments help to overcome the local sea air. Many sanatoriums have been built on the seashore in Dagestan. People here improve their health with mineral waters, mud, curative climate. Not without health and sports tourism. Leisure quite popular today. For those who wish, extreme, skiing, ecological tourism is offered. You can be sure that the Caspian Sea and its coastal areas deserve to be visited.
Caspian Sea - the largest lake on Earth, drainless, located at the junction of Europe and Asia, called the sea because of its size, and also because its bed is composed of oceanic-type earth's crust. The water in the Caspian is salty - from 0.05 ‰ near the mouth of the Volga to 11-13 ‰ in the southeast. The water level is subject to fluctuations, according to 2009 data it was 27.16 m below sea level. The area of the Caspian Sea is currently approximately 371,000 km², the maximum depth is 1025 m.
Geographical position
The Caspian Sea is located at the junction of two parts of the Eurasian continent - Europe and Asia. The length of the Caspian Sea from north to south is approximately 1200 kilometers (36°34 "-47°13" N), from west to east - from 195 to 435 kilometers, on average 310-320 kilometers (46°-56° v. d.). The Caspian Sea is conditionally divided according to physical and geographical conditions into 3 parts - the Northern Caspian, the Middle Caspian and the Southern Caspian. The conditional border between the North and Middle Caspian runs along the line of about. Chechnya - Cape Tyub-Karagansky, between the Middle and South Caspian - along the line of about. Residential - Cape Gan-Gulu. The area of the Northern, Middle and Southern Caspian is 25, 36, 39 percent respectively.
The length of the coastline of the Caspian Sea is estimated at about 6500-6700 kilometers, with islands - up to 7000 kilometers. The shores of the Caspian Sea in most of its territory are low-lying and smooth. In the northern part, the coastline is indented by water channels and islands of the Volga and Ural deltas, the shores are low and swampy, and the water surface is covered with thickets in many places. The east coast is dominated by limestone shores adjacent to semi-deserts and deserts. The most winding coasts are on the west coast in the area of the Apsheron Peninsula and on the east coast in the area of the Kazakh Gulf and Kara-Bogaz-Gol. The territory adjacent to the Caspian Sea is called the Caspian Sea.
Peninsulas of the Caspian Sea
Large peninsulas of the Caspian Sea:
- Agrakhan Peninsula
- The Absheron Peninsula, located on the western coast of the Caspian Sea in the territory of Azerbaijan, at the northeastern end of the Greater Caucasus, the cities of Baku and Sumgayit are located on its territory
- Buzachi
- Mangyshlak, located on the eastern coast of the Caspian Sea, on the territory of Kazakhstan, on its territory is the city of Aktau
- Miankale
- Tyub-Karagan
Islands of the Caspian Sea
There are about 50 large and medium-sized islands in the Caspian Sea with a total area of approximately 350 square kilometers. The largest islands:
- Ashur-Ada
- Garasu
- Boyuk Zira
- Zyanbil
- Cure Dashi
- Hara Zira
- Ogurchinsky
- Sengi-Mugan
- Seals
- Seal Islands
- Chechen
- Chygyl
Bays of the Caspian Sea
Large bays of the Caspian Sea:
- Agrakhan bay
- Kizlyar Bay
- Dead Kultuk (former Komsomolets, former Tsesarevich Bay)
- Kaydak
- Mangyshlak
- Kazakh
- Kenderly
- Turkmenbashi (bay) (former Krasnovodsk)
- Turkmen (bay)
- Gyzylagach (former bay named after Kirov)
- Astrakhan (bay)
- Hasan-kuli
- Gyzlar
- Hyrcanus (former Astarabad)
- Anzali (former Pahlavi)
- Kara-Bogaz-Gol
Rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea- 130 rivers flow into the Caspian Sea, of which 9 rivers have a mouth in the form of a delta. The major rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea are the Volga, Terek, Sulak, Samur (Russia), Ural, Emba (Kazakhstan), Kura (Azerbaijan), Atrek (Turkmenistan), Sefidrud (Iran) and others. The largest river flowing into the Caspian Sea is the Volga, its average annual runoff is 215-224 cubic kilometers. The Volga, Ural, Terek, Sulak and Emba provide up to 88-90% of the annual runoff to the Caspian Sea.
Physiography
Area, depth, volume of water- The area and volume of water in the Caspian Sea varies significantly depending on fluctuations in water levels. At a water level of -26.75 m, the area is approximately 371,000 square kilometers, the volume of water is 78,648 cubic kilometers, which is approximately 44% of the world's lake water reserves. The maximum depth of the Caspian Sea is in the South Caspian depression, 1025 meters from its surface level. In terms of maximum depth, the Caspian Sea is second only to Baikal (1620 m) and Tanganyika (1435 m). The average depth of the Caspian Sea, calculated from the bathygraphic curve, is 208 meters. At the same time, the northern part of the Caspian Sea is shallow, its maximum depth does not exceed 25 meters, and the average depth is 4 meters.
Water level fluctuations- The water level in the Caspian Sea is subject to significant fluctuations. According to modern science, over the past three thousand years, the magnitude of the change in the water level of the Caspian Sea has reached 15 meters. According to archeology and written sources, a high level of the Caspian Sea is recorded at the beginning of the 14th century. Instrumental measurement of the level of the Caspian Sea and systematic observations of its fluctuations have been carried out since 1837, during this time the highest water level was recorded in 1882 (−25.2 m), the lowest - in 1977 (−29.0 m), from In 1978, the water level rose and in 1995 it reached -26.7 m, since 1996 there has been a downward trend again. Scientists associate the causes of changes in the water level of the Caspian Sea with climatic, geological and anthropogenic factors. But in 2001, the sea level began to rise again, and reached -26.3 m.
Water temperature- water temperature is subject to significant latitudinal changes, most clearly expressed in winter period when the temperature changes from 0-0.5 °C at the ice edge in the north of the sea to 10-11 °C in the south, that is, the water temperature difference is about 10 °C. For shallow water areas with depths less than 25 m, the annual amplitude can reach 25-26 °C. On average, the water temperature near the western coast is 1-2 °C higher than that of the eastern one, and in the open sea the water temperature is 2-4 °C higher than near the coasts.
Water composition- the salt composition of the waters of the closed Caspian Sea differs from that of the ocean. There are significant differences in the ratios of the concentrations of salt-forming ions, especially for the waters of areas under the direct influence of continental runoff. The process of metamorphization of sea waters under the influence of continental runoff leads to a decrease in the relative content of chlorides in the total amount of salts in sea waters, an increase in the relative amount of carbonates, sulfates, and calcium, which are the main components in the chemical composition of river waters. The most conservative ions are potassium, sodium, chloride and magnesium. The least conservative are calcium and bicarbonate ion. In the Caspian Sea, the content of calcium and magnesium cations is almost two times higher than in the Sea of Azov, and sulfate anion is three times higher.
Bottom relief- the relief of the northern part of the Caspian Sea is a shallow wavy plain with banks and accumulative islands, the average depth of the Northern Caspian is 4-8 meters, the maximum does not exceed 25 meters. The Mangyshlak threshold separates the Northern Caspian from the Middle. The Middle Caspian is quite deep, the depth of water in the Derbent depression reaches 788 meters. The Apsheron threshold separates the Middle and South Caspian. The South Caspian is considered deep water, the depth of water in the South Caspian depression reaches 1025 meters from the surface of the Caspian Sea. Shell sands are common on the Caspian shelf, deep-water areas are covered with silty sediments, and in some areas there is an outcrop of bedrock.
Climate- The climate of the Caspian Sea is continental in the northern part, temperate in the middle part and subtropical in the southern part. In winter, the average monthly air temperature varies from -8…-10 in the northern part to +8…+10 in the southern part, in summer - from +24…+25 in the northern part to +26…+27 in the southern part. The maximum temperature of +44 degrees was recorded on the east coast. The average annual rainfall is 200 millimeters, ranging from 90-100 millimeters in the arid eastern part to 1,700 millimeters off the southwestern subtropical coast. Evaporation of water from the surface of the Caspian Sea is about 1000 millimeters per year, the most intense evaporation in the area of the Absheron Peninsula and in the eastern part of the South Caspian is up to 1400 millimeters per year. The average annual wind speed is 3-7 meters per second, northerly winds prevail in the wind rose. In the autumn and winter months, the winds increase, the wind speed often reaches 35-40 meters per second. The most windy areas are the Apsheron Peninsula, the environs of Makhachkala and Derbent, where the highest wave 11 meters high was also recorded.
currents- The circulation of waters in the Caspian Sea is connected with the runoff and winds. Since most of the water flow falls on the Northern Caspian, the northern currents predominate. An intense northern current carries water from the Northern Caspian along the western coast to the Absheron Peninsula, where the current is divided into two branches, one of which moves further along the western coast, the other goes to the Eastern Caspian.
Economic development of the Caspian Sea
Mining of oil and gas-Many oil and gas fields are being developed in the Caspian Sea. The proven oil resources in the Caspian Sea are about 10 billion tons, the total resources of oil and gas condensate are estimated at 18-20 billion tons. Oil production in the Caspian Sea began in 1820, when the first oil well was drilled on the Absheron shelf near Baku. In the second half of the 19th century, oil production began on an industrial scale on the Absheron Peninsula, and then on other territories. In 1949, Oil Rocks for the first time began to extract oil from the bottom of the Caspian Sea. So, on August 24 of this year, the team of Mikhail Kaverochkin started drilling a well, which on November 7 of the same year gave the long-awaited oil. In addition to oil and gas production, salt, limestone, stone, sand, and clay are also mined on the coast of the Caspian Sea and the Caspian shelf.
Shipping- Shipping is developed in the Caspian Sea. Ferry crossings operate on the Caspian Sea, in particular, Baku - Turkmenbashi, Baku - Aktau, Makhachkala - Aktau. The Caspian Sea has a navigable connection with the Sea of Azov through the Volga and Don rivers and the Volga-Don Canal.
Fishing and seafood-fishing (sturgeon, bream, carp, pike perch, sprat), caviar production, as well as seal fishing. More than 90 percent of the world's sturgeon catch is carried out in the Caspian Sea. In addition to industrial production, illegal production of sturgeon and their caviar flourishes in the Caspian Sea.
Legal status of the Caspian Sea- after the collapse of the USSR, the division of the Caspian Sea has long been and still remains the subject of unsettled disagreements related to the division of the resources of the Caspian shelf - oil and gas, as well as biological resources. For a long time there were negotiations between littoral states on the status of the Caspian Sea - Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan insisted on dividing the Caspian along the median line, Iran - on dividing the Caspian along one fifth between all the Caspian states. The current legal regime of the Caspian is established by the Soviet-Iranian treaties of 1921 and 1940. These treaties provide for freedom of navigation throughout the sea, freedom of fishing, with the exception of ten-mile national fishing zones, and a ban on navigation in its waters of ships flying the flag of non-Caspian states. Negotiations on the legal status of the Caspian are currently ongoing.
The Caspian Lake is one of the most unique places on the ground. It keeps many secrets connected with the history of the development of our planet.
Position on the physical map
The Caspian is an internal drainless salt lake. The geographical position of the Caspian Lake is the continent of Eurasia at the junction of parts of the world (Europe and Asia).
The length of the lakeshore line is from 6500 km to 6700 km. Taking into account the islands, the length increases to 7000 km.
The coastal areas of the Caspian Lake are mostly low-lying. Their northern part is indented by the channels of the Volga and the Urals. The river delta is rich in islands. The surface of the water in these areas is covered with thickets. Swampiness of large areas of land is noted.
The eastern coast of the Caspian adjoins to the lake. There are significant limestone deposits on the shores of the lake. The western and part of the eastern coast is characterized by a winding coastline.
The Caspian lake on the map is represented by a significant size. The entire territory adjacent to it was called the Caspian Sea.
Some characteristics
The Caspian Lake in terms of its area and the volume of water in it has no equal on Earth. It stretches from north to south for 1049 kilometers, and its longest length from west to east is 435 kilometers.

If we take into account the depth of reservoirs, their area and volume of water, then the lake is commensurate with the Yellow, Baltic and Black Seas. By the same parameters, the Caspian surpasses the Tyrrhenian, Aegean, Adriatic and other seas.
The volume of water available in the Caspian Lake is 44% of the reserve of all lake waters of the planet.
Lake or sea?
Why is the Caspian lake called the sea? Is it really the impressive size of the reservoir that caused the assignment of such a “status”? More precisely, this was one of those reasons.
Others include a huge mass of water in the lake, the presence of a large wave during storm winds. All this is typical for real seas. It becomes clear why the Caspian Lake is called the sea.
But here one of the main conditions is not named, which must necessarily exist so that geographers can classify a reservoir as a sea. We are talking about the direct connection of the lake with the oceans. The Caspian does not meet this condition.
Where the Caspian Lake is located, a deepening in the earth's crust was formed several tens of thousands of years ago. Today it is filled with the waters of the Caspian Sea. According to scientists, at the end of the 20th century, the water level in the Caspian Sea was 28 meters below the level of the World Ocean. The direct connection of the waters of the lake and the ocean ceased to exist approximately 6 millennia ago. The conclusion from the above is that the Caspian Sea is a lake.
There is another feature that distinguishes the Caspian Sea from the sea - the salinity of the water in it is almost 3 times lower than the salinity of the World Ocean. The explanation for this is that about 130 large and small rivers carry fresh water to the Caspian Sea. The Volga makes the most significant contribution to this work - it is she who “gives” up to 80% of all water to the lake.
The river played another important role in the life of the Caspian Sea. It is she who will help find the answer to the question of why the Caspian Lake is called the sea. Now that many channels have been built by man, it has become a fact that the Volga connects the lake with the oceans.
The history of the lake
modern look and geographical position The Caspian lake is caused by continuous processes occurring on the surface of the Earth and in its bowels. There were times when the Caspian was connected with the Sea of Azov, and through it with the Mediterranean and Black. That is, tens of thousands of years ago, the Caspian Lake was part of the World Ocean.

As a result of the processes associated with the uplift and lowering of the earth's crust, mountains appeared on the site of the modern Caucasus. They isolated a body of water that was part of a vast ancient ocean. More than one tens of thousands of years passed before the basins of the Black and Caspian Seas separated. But for a long time, the connection between their waters was carried out through the strait, which was on the site of the Kumo-Manych depression.
Periodically, the narrow strait was either drained or refilled with water. This was due to fluctuations in the level of the oceans and changes in the appearance of the land.
In a word, the origin of the Caspian Lake is closely connected with the general history of the formation of the Earth's surface.
The lake got its modern name because of the tribes of the Caspians, who inhabited the eastern parts of the Caucasus and the steppe zones of the Caspian territories. Over the entire history of its existence, the lake had 70 different names.
Territorial division of the lake-sea
The depth of the Caspian Lake in its different places is very different. Based on this, the entire water area of the lake-sea was conditionally divided into three parts: the Northern Caspian, the Middle and the Southern.

Shallow - this is the northern part of the lake. The average depth of these places is 4.4 meters. The highest indicator is a mark of 27 meters. And on 20% of the entire area of the Northern Caspian, the depth is only about a meter. It is clear that this part of the lake is of little use for navigation.
The Middle Caspian has the greatest depth of 788 meters. The deep part occupies lakes. The average depth here is 345 meters, and the greatest is 1026 meters.
Seasonal changes at sea
Due to the large length of the reservoir from north to south climatic conditions on the coast of the lake are not the same. Seasonal changes in the territories adjacent to the reservoir also depend on this.

In winter, on the southern coast of the lake in Iran, the water temperature does not drop below 13 degrees. During the same period, in the northern part of the lake off the coast of Russia, the water temperature does not exceed 0 degrees. The Northern Caspian is covered with ice during 2-3 months of the year.
In summer, almost everywhere the Caspian Lake warms up to 25-30 degrees. Warm water, great sandy beaches, sunny weather create excellent conditions for people to relax.
Caspian on the political map of the world
Five states are located on the shores of the Caspian Lake - Russia, Iran, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan.
The territory of Russia includes the western regions of the Northern and Middle Caspian. Iran is located on the southern shores of the sea, it owns 15% of the entire length of the coastline. Eastern line The coasts are shared by Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan. Azerbaijan is located in the southwestern territories of the Caspian Sea.
The issue of dividing the water area of the lake between the Caspian states has been the most acute for many years. The heads of the five states are trying to find a solution that would satisfy the needs and requirements of everyone.
The natural wealth of the lake
Caspian from ancient times for local residents served as a waterway.

The lake is famous for its valuable species of fish, in particular sturgeon. Their reserves account for up to 80% of the world's resources. The issue of preserving the sturgeon population is of international importance, it is solved at the level of the government of the Caspian states.
The Caspian seal is another mystery of the unique sea-lake. Scientists have not yet fully unraveled the mystery of the appearance of this animal in the waters of the Caspian Sea, as well as other species of animals of northern latitudes.
In total, 1809 species of various groups of animals live in the Caspian Sea. There are 728 species of plants. Most of them are the "indigenous inhabitants" of the lake. But there is a small group of plants that were deliberately brought here by man.
Of the minerals, the main wealth of the Caspian is oil and gas. Some information sources compare the oil reserves of the Caspian Lake fields with Kuwait. Industrial marine mining of black gold has been carried out on the lake since the end of the 19th century. The first well appeared on the Apsheron shelf in 1820.
Today, the governments unanimously believe that the region cannot be considered only as a source of oil and gas, while leaving the Caspian ecology unattended.
In addition to oil fields, there are deposits of salt, stone, limestone, clay and sand on the territory of the Caspian Sea. Their extraction also could not but affect the ecological situation of the region.
Sea level fluctuations
The water level in the Caspian Lake is not constant. This is evidenced by evidence relating to the IV century BC. The ancient Greeks who explored the sea discovered big bay at the confluence of the Volga. The existence of a shallow strait between the Caspian and the Sea of Azov was also discovered by them.

There are other data on the water level in the Caspian Lake. The facts show that the level was much lower than it is now. The evidence is ancient architectural structures found on the seabed. The buildings date back to the 7th-13th centuries. Now the depth of their flooding is from 2 to 7 meters.
In 1930, the water level in the lake began to decline catastrophically. The process went on for almost fifty years. This caused great concern among people, since all the economic activities of the Caspian region are adapted to the previously established water level.
Since 1978 the level has started to rise again. Today it has become more than 2 meters taller. This is also an undesirable phenomenon for people living on the coast of the lake-sea.
Climate change is said to be the main reason for fluctuations in the lake. This entails an increase in the volume of river water entering the Caspian, the amount of precipitation, and a decrease in the intensity of water evaporation.
However, it cannot be said that this is the only opinion that explains the fluctuations in the water level in the Caspian Lake. There are others, no less plausible.
Human activities and environmental issues
The area of the catchment basin of the Caspian Lake is 10 times larger than the surface of the water area of the reservoir itself. Therefore, all the changes taking place in such a vast territory in one way or another affect the ecology of the Caspian Sea.
Human activity plays an important role in changing the ecological situation in the area of the Caspian Lake. For example, pollution of a reservoir with harmful and hazardous substances occurs along with the influx fresh water. This is directly related to industrial production, mining and other human activities in the catchment area.
State environment The Caspian Sea and the territories adjacent to it are of general concern to the governments of the countries located here. Therefore, the discussion of measures aimed at preserving unique lake, its flora and fauna, has become traditional.
Each state has an understanding that only through joint efforts can the ecology of the Caspian Sea be improved.
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on the planet Earth, located on the continent of Eurasia - in border area states Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran and Azerbaijan. In fact, it is a giant lake left after the disappearance of the ancient Tethys ocean. Nevertheless, there is every reason to consider it as an independent sea (this is indicated by salinity, a large area and decent depth, the bottom of the oceanic crust and other signs). In terms of maximum depth, it is the third among closed reservoirs - after lakes Baikal and Tanganyika. In the northern part of the Caspian Sea (a few kilometers from the northern coast - parallel to it) there is a geographical border between Europe and Asia.
Toponymy
- Other names: throughout the history of mankind, different peoples of the Caspian Sea had about 70 different names. The most famous of them are: Khvalynskoe or Khvalisskoe (it took place during Ancient Rus', arose on behalf of the people praise, who lived in the Northern Caspian and traded with the Russians), Girkan or Dzhurdzhan (derived from the alternative names of the city of Gorgan, located in Iran), Khazar, Abeskun (after the name of the island and city in the Kura delta - now flooded), Saray, Derbent, Sikhay .
- Origin of name: according to one of the hypotheses, the Caspian Sea received its modern and most ancient name from a tribe of nomadic horse breeders the Caspians who lived in the 1st millennium BC on the southwestern coast.
Morphometry
- Catchment area: 3,626,000 km².
- Mirror area: 371,000 km².
- Coastline length: 7,000 km.
- Volume: 78,200 km³.
- Average depth: 208 m
- Max Depth: 1025 m.
Hydrology
- The presence of a constant flow: no, it's pointless.
- Tributaries:, Ural, Emba, Atrek, Gorgan, Heraz, Sefidrud, Astarchay, Kura, Pirsagat, Kusarchay, Samur, Rubas, Darvagchay, Ulluchay, Shuraozen, Sulak, Terek, Kuma.
- Bottom: very varied. At shallow depths, sandy soil with an admixture of shells is common, in deep water places - silty. Pebble and rocky places can be found in the coastal strip (especially where mountain ranges adjoin the sea). In the estuarine areas, the underwater soil consists of river sediments. The Kara-Bogaz-Gol bay is notable for the fact that its bottom is a powerful layer of mineral salts.
Chemical composition
- Water: brackish.
- Salinity: 13 g / l.
- Transparency: 15 m.
Geography

Rice. 1. Map of the Caspian Sea basin.
- Coordinates: 41°59′02″ s. sh., 51°03′52″ E d.
- Height above sea level:-28 m.
- Coastal landscape: Due to the fact that the coastline of the Caspian Sea is very long, and it is located in different geographical zones, the coastal landscape is diverse. In the northern part of the reservoir, the shores are low, swampy, in places of the deltas of large rivers they are indented by numerous channels. The eastern shores are mostly limestone - desert or semi-desert. Western and south coast adjacent to mountain ranges. The greatest indentation of the coastline is observed in the west - in the area of the Apsheron Peninsula, as well as in the east - in the area of the Kazakh and Kara-Bogaz-Gol bays.
- Settlements on the coast:
- Russia: Astrakhan, Derbent, Kaspiysk, Makhachkala, Olya.
- Kazakhstan: Aktau, Atyrau, Kuryk, Sogandyk, Bautino.
- Turkmenistan: Ekerem, Karabogaz, Turkmenbashi, Khazar.
- Iran: Astara, Balboser, Bender-Torkemen, Bender-Anzeli, Neka, Chalus.
- Azerbaijan: Alyat, Astara, Baku, Dubendi, Lankaran, Sangachali, Sumgayit.
interactive map
Ecology
The ecological situation in the Caspian Sea is far from ideal. Almost all large rivers flowing into it are polluted by the effluents of industrial enterprises located upstream. This could not but affect the presence of pollutants in the waters and bottom sediments of the Caspian - over the past half century, their concentration has increased markedly, and the content of some heavy metals has already exceeded the permissible limits.
In addition, the waters of the Caspian Sea are constantly polluted by domestic wastewater from coastal cities, as well as during oil production on the continental shelf, and during its transportation.
Fishing in the Caspian Sea
- Fish species:
- Artificial settlement: not all of the above fish species in the Caspian Sea are native. About 4 dozen species came by chance (for example, through channels from the basins of the Black and Baltic Seas), or were deliberately populated by humans. An example is the mullet. Three Black Sea species of these fish - striped mullet, sharp-nosed mullet and golden mullet - were released in the first half of the 20th century. The striped mullet did not take root, but the blackfin with golden mullet have successfully acclimatized, and by the current moment they have settled in virtually the entire Caspian water area, having formed several commercial herds. At the same time, fish feed faster than in the Black Sea, and reach larger sizes. In the second half of the last century (since 1962), attempts were also made to populate such Far Eastern salmon fish as pink salmon and chum salmon in the Caspian Sea. In total, several billion fry of these fish were released into the sea within 5 years. Pink salmon did not survive in the new range, but on the contrary, chum salmon successfully took root and even began to spawn in the rivers flowing into the sea. However, she could not reproduce in sufficient quantities and gradually disappeared. There are as yet no favorable conditions for its full-fledged natural reproduction (there are very few places where spawning and development of fry could successfully occur). To ensure them, river reclamation is needed, otherwise, without human help (artificial sampling of eggs and its incubation), fish will not be able to maintain their numbers.
Fishing places
In fact, fishing is possible at any point on the coast of the Caspian Sea, which can be reached by land or water. Which species of fish will be caught at the same time depends on local conditions, but to a greater extent on whether rivers flow here. As a rule, in places where estuaries and deltas (especially large watercourses) are located, the water in the sea is strongly desalinated, therefore, freshwater fish (carp, catfish, bream, etc.) usually predominate in catches; rivers (barbels, shemaya). From marine species in desalinated areas, those for which salinity does not matter are caught (mullet, some of the gobies). In certain periods of the year, semi-anadromous and migratory species can be found here, feeding in the sea, and entering the rivers for spawning (sturgeon, some of herring, Caspian salmon). In places where there are no flowing rivers, freshwater species are found in a slightly smaller number, but at the same time, marine fish appear, usually avoiding desalinated areas (for example, sea zander). Away from the coast, fish that prefer salt water and deep-sea species are caught.
Conventionally, 9 places or areas of interest in terms of fishing can be distinguished:
- North Shore (RF)- this area is located on the northern coast of the Russian Federation (from the Volga delta to the Kizlyar Bay). Its main features are the insignificant salinity of the water (the lowest in the Caspian Sea), shallow depth, the presence of multiple shoals, islands, and highly developed aquatic vegetation. In addition to the Volga delta with its numerous channels, bays and erics, it also includes the estuarine seaside, called the Caspian peals. These places are popular with Russian fishermen, and for good reason: the conditions for fish are very favorable here, and there is also a good forage base. The ichthyofauna in these parts may not shine with a richness of species, but it is distinguished by its abundance, and some of its representatives reach a very considerable size. Usually the basis of catches are freshwater fish, typical for the Volga basin. Most often caught: perch, pike perch, roach (more precisely, its varieties, called roach and ram), rudd, asp, sabrefish, bream, goldfish, carp, catfish, pike. Bursh, silver bream, white-eye, blue bream are somewhat less common. There are also representatives of sturgeon (sturgeon, stellate sturgeon, beluga, etc.), salmon (nelma, brown trout - Caspian salmon) in these places, but their catch is prohibited.
- Northwestern coast (RF)- this area covers West Coast Russian Federation(from Kizlyar Bay to Makhachkala). The Kuma, Terek and Sulak rivers flow here - they carry their waters both along natural channels and artificial channels. In this area there are bays, among which are quite large ones (Kizlyarsky, Agrakhansky). The sea in these places is shallow. Of the fish in the catches, freshwater species predominate: pike, perch, carp, catfish, rudd, bream, barbel, etc., marine species are also caught here, for example, herring (black-backed, shad).
- West Bank (RF)- from Makhachkala to the border of the Russian Federation with Azerbaijan. An area where mountain ranges adjoin the sea. The salinity of the water here is somewhat higher than in previous places, therefore, marine species are more common in the catches of fishermen (sea pike, mullet, herring). However, freshwater fish are by no means uncommon.
- West Bank (Azerbaijan)- from the border of the Russian Federation with Azerbaijan to the Absheron Peninsula. Continuation of the section where mountain ranges adjoin the sea. Fishing here is even more similar to typical sea fishing, thanks to fish such as hart and golden mullet (mullet) and several types of gobies, which are also caught here. In addition to them, there are kutum, herring, and some typically freshwater species, for example, carp.
- Southwest coast (Azerbaijan)- from the Absheron Peninsula to the border of Azerbaijan with Iran. Most of this area is occupied by the delta of the Kura River. Here the same species of fish are caught that were listed in the previous paragraph, but freshwater ones are somewhat more common.
- North Shore (Kazakhstan)- this area covers north coast Kazakhstan. The Ural delta and the Akzhaiyk state reserve are located here, therefore fishing directly in the river delta and in some waters adjacent to it is prohibited. Fishing is possible only outside the reserve - upstream from the delta, or in the sea - at some distance from it. Fishing near the Ural delta has much in common with fishing at the confluence of the Volga - almost the same species of fish are found here.
- Northeast coast (Kazakhstan)- from the mouth of the Emba to Cape Tyub-Karagan. In contrast to the northern part of the sea, where the water is greatly diluted by large rivers flowing into it, its salinity is slightly increased here, therefore, those fish species appear that avoid desalinated areas, for example, sea zander, which is caught in the Dead Kultuk Bay. Also, other representatives of marine fauna are often found in the catches.
- Eastern coast (Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan)- from Cape Tyub-Karagan to the border of Turkmenistan and Iran. Differs in the almost complete absence of flowing rivers. The salinity of the water here is at its highest. Of the fish in these places, marine species predominate, the main catches are mullet, pike perch and gobies.
- South Shore (Iran)- covers the southern coast of the Caspian Sea. Throughout this section, the Elburs mountain range adjoins the sea. Many rivers flow here, most of which are represented by small streams, there are also several medium ones and one major river. Of the fish, in addition to marine species, there are also some freshwater, as well as semi-anadromous and anadromous species, for example, sturgeons.
Features of fishing
The most popular and catchy amateur tackle that is used on the Caspian coast is a heavy spinning rod converted into a “sea bottom”. Usually it is equipped with a strong spool, on which a fairly thick line (0.3 mm or more) is wound. The thickness of the fishing line is determined not so much by the size of the fish as by the mass of a rather heavy sinker, which is necessary for an ultra-long cast (in the Caspian it is widely believed that the farther from the shore the casting point is, the better). After the sinker comes a thinner fishing line - with several leashes. As a bait, shrimps and amphipods that live in coastal thickets of algae are used - if it is supposed to catch sea fish, or an ordinary bait like a worm, cockchafer larvae and others - if freshwater species are found in the fishing area.
In estuaries of inflowing rivers, other tackle such as float rod, feeder and traditional spinning can be used.
kasparova2 majorov2006 g2gg2g-61 .

Photo 8. Sunset in Aktau.
The Caspian Sea is one of the largest salt water bodies of the Earth, located at the junction of Europe and Asia. Its total area is about 370 thousand square meters. km. The reservoir accepts more than 100 water streams. The largest rivers flowing into - Volga, Ural, Emba, Terek, Sulak, Samur, Kura, Atrek, Sefidrud.
The Volga River - the pearl of Russia
The Volga is a river that flows through the territory of the Russian Federation and partially crosses Kazakhstan. It belongs to the category of the largest and longest rivers on Earth. The total length of the Volga is more than 3500 km. The river originates in the village of Volgoverkhovye, Tver region, located on the territory of the Russian Federation. After that, it continues its movement through the territory of the Russian Federation.
It flows into the Caspian Sea, but does not have a direct outlet to the World Ocean, so it is classified as an internal drain. The watercourse receives about 200 tributaries and has more than 150 thousand drains. Today, reservoirs have been built on the river, allowing to regulate the flow, due to which the fluctuations in the water level have been sharply reduced.
The fishery of the river is diverse. Melon growing prevails in the Volga region: the fields are occupied by grain and industrial crops; salt is mined. Oil and gas fields have been discovered in the Ural region. The Volga is the largest river flowing into the Caspian Sea, so it is of great importance for Russia. The main transport facility that allows crossing this stream is the longest one in Russia.
Ural - a river in Eastern Europe
The Ural, like the Volga River, flows on the territory of two states - Kazakhstan and the Russian Federation. Historical name - Yaik. It originates in Bashkortostan at the top of the Uraltau ridge. The Ural River flows into the Caspian Sea. Its basin is the sixth largest in the Russian Federation, and the area is more than 230 square meters. km. Interesting fact: the Ural River, contrary to popular belief, belongs to the inland European river, and only its upper course in Russia belongs to Asia.
The mouth of the stream gradually becomes shallower. At this point, the river splits into several branches. This feature is typical throughout the entire length of the channel. During floods, you can watch the Ural overflow its banks, in principle, like many other Russian rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea. This is especially observed in places with a gently sloping coastline. Flooding occurs at a distance of up to 7 meters from the riverbed.

Emba - the river of Kazakhstan
Emba is a river flowing on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The name comes from the Turkmen language, literally translated as "the valley of food." The river basin with an area of 40 thousand square meters. km. The river begins its journey in the mountains of Mugodzhary and, flowing along, is lost among the swamps. Asking which rivers flow into the Caspian Sea, we can say that in full-flowing years, the Emba reaches its basin.
Natural resources such as oil and gas are being exploited along the coastline of the river. The issue of passing the border between Europe and Asia along the Emba watercourse, as in the case of the river. Ural, an open topic today. The reason for this is a natural factor: the mountains of the Ural Range, which are the main reference point for drawing borders, disappear, forming a homogeneous area.
Terek - mountain water stream
Terek - river North Caucasus. The name literally translates from Turkic as "poplar". The Terek flows out of the glacier of Mount Zilga-Khokh, located in the Trusovsky Gorge of the Caucasus Range. passes through the lands of many states: North Ossetia, Georgia, Stavropol Territory, Kabardino-Balkaria, Dagestan and the Chechen Republic. It flows into the Caspian Sea and the Arkhangelsk Bay. The length of the river is just over 600 km, the basin area is about 43 thousand square meters. km. An interesting fact is that every 60-70 years the flow forms a new transit arm, while the old one loses its strength and disappears.
The Terek, like other rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea, is widely used to satisfy human economic needs: it is used to irrigate the arid territories of the adjacent lowlands. There are also several hydroelectric power plants on the water stream, the total average annual output of which is more than 200 million kWh. In the near future, it is planned to launch additional additional stations.

Sulak - water stream of Dagestan
Sulak is a river that connects the streams of the Avar Koisu and the Andi Koisu. It flows through the territory of Dagestan. It starts in the Main Sulak Canyon and ends its journey in the waters of the Caspian Sea. The main purpose of the river is the water supply of two cities of Dagestan - Makhachkala and Kaspiysk. Also, several hydroelectric power stations are already located on the river, it is planned to launch new ones to increase the generated capacity.
Samur - the pearl of South Dagestan
Samur is the second largest river in Dagestan. Literally, the name from the Indo-Aryan is translated as "an abundance of water." It originates at the foot of Mount Guton; It flows into the waters of the Caspian Sea in two branches - Samur and Small Samur. The total length of the river is just over 200 km.
All rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea are of great importance for the territories through which they flow. Samur is no exception. The main direction of using the river is irrigation of lands and providing residents of nearby cities with drinking water. It was because of this that a hydroelectric complex and a number of the Samur-Divichinsky canal were built.
At the beginning of the 20th century (2010), Russia and Azerbaijan signed an interstate agreement requiring both sides to rationally use the resources of the Samur River. The same agreement introduced territorial changes between these countries. The border between the two states has been moved to the middle of the hydroelectric complex.

Kura - the largest river of Transcaucasia
Asking the question which rivers flow into the Caspian Sea, I want to describe the flow of the Kuru. It flows on the land of three states at once: Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan. The length of the stream is more than 1000 km, the total area of the basin is about 200 thousand square meters. km. Part of the basin is located on the territory of Armenia and Iran. The source of the river is located in the Turkish province of Kars, flows into the waters of the Caspian Sea. The path of the river is thorny, laid among hollows and gorges, for which it got its name, which in Megrelian means “nibble”, that is, the Kura is a river that “gnaws” itself even among the mountains.
There are many cities on it, such as Borjomi, Tbilisi, Mtskheta and others. It plays an important role in meeting the economic needs of the inhabitants of these cities: hydroelectric power stations are located, and the Mingachevir reservoir created on the river is one of the main fresh water reserves for Azerbaijan. Unfortunately, the ecological state of the stream leaves much to be desired: the level of harmful substances exceeds the permissible limits by several times.

Features of the Atrek River
Atrek is a river located on the territory of Iran and Turkmenistan. It originates in the Turkmen-Kharasan mountains. Due to the active use in economic needs for irrigation of land, the river became shallow. For this reason, it reaches the Caspian Sea only during the flood period.
Sefidrud - the abundant river of the Caspian
Sefidrud is a major river of the Iranian state. It was originally formed by the confluence of two water streams - Kyzyluzen and Shakhrud. Now it flows out of the Shabanau reservoir and flows into the depths of the Caspian Sea. The total length of the river is over 700 km. The creation of a reservoir has become a necessity. It made it possible to minimize the risks of flooding, thereby securing the cities located in the river delta. The waters are used for irrigation of land with a total area of more than 200 thousand hectares of land.

As can be seen from the presented material, the Earth's water resources are in an unsatisfactory state. The rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea are actively used by man to meet his needs. And this has a detrimental effect on their condition: watercourses are depleted and polluted. That is why scientists around the world are sounding the alarm and conducting active propaganda, calling for saving and conserving water on Earth.